Download Docker Toolbox For Windows 10 Pro
- Windows: Docker Desktop 2.0+ on Windows 10 Pro/Enterprise. Windows 10 Home (2004+) requires Docker Desktop 2.3+ and the WSL 2 back-end. (Docker Toolbox is not supported. Windows container images are not supported.) macOS: Docker Desktop 2.0+. Linux: Docker CE/EE 18.06+ and Docker Compose 1.21+. (The Ubuntu snap package is not supported.
- In this tutorial, I am going to show you how to install Minikube on Windows 10 operating system. How to install Minikube on Windows 10: Installing Minikube on Windows 10 is a simple process; here I am providing an easy technique to install minikube along with kubeadm and kubectl on windows.
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
If you have a newer system, specifically 64bit Windows 10 Pro, with Enterprise and Education (1511 November update, Build 10586 or later), consider using Docker for Windows instead. It runs natively on the Windows, so there is no need for a pre-configured Docker QuickStart shell.
Docker Desktop for Windows is the Community version of Docker for Microsoft Windows.You can download Docker Desktop for Windows from Docker Hub.
By downloading Docker Desktop, you agree to the terms of the Docker Software End User License Agreement and the Docker Data Processing Agreement.
System requirements
Your Windows machine must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop.
Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, or Education (Build 17134 or higher).
For Windows 10 Home, see System requirements for WSL 2 backend.
- Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled.
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run ClientHyper-V on Windows 10:
- 64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in theBIOS settings. For more information, seeVirtualization.
WSL 2 backend
Download Docker Toolbox For Windows 10 Product
- Windows 10 64-bit: Home, Pro, Enterprise, or Education, version 1903 (Build 18362 or higher).
- Enable the WSL 2 feature on Windows. For detailed instructions, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully runWSL 2 on Windows 10:
- 64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in theBIOS settings. For more information, seeVirtualization.
- Download and install the Linux kernel update package.
Note
Docker supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine,Docker CLI client, Docker Compose,Notary,Kubernetes,and Credential Helper.
Containers and images created with Docker Desktop are shared between alluser accounts on machines where it is installed. This is because all Windowsaccounts use the same VM to build and run containers. Note that it is not possible to share containers and images between user accounts when using the Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend.
Nested virtualization scenarios, such as running Docker Desktop on aVMWare or Parallels instance might work, but there are no guarantees. Formore information, see Running Docker Desktop in nested virtualization scenarios.
About Windows containers
Looking for information on using Windows containers?
- Switch between Windows and Linux containersdescribes how you can toggle between Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop and points you to the tutorial mentioned above.
- Getting Started with Windows Containers (Lab)provides a tutorial on how to set up and run Windows containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. It shows you how to use a MusicStore applicationwith Windows containers.
- Docker Container Platform for Windows articles and blogposts on the Docker website.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer.
If you haven’t already downloaded the installer (
Docker Desktop Installer.exe), you can get it from Docker Hub. It typically downloads to yourDownloadsfolder, or you can run it from the recent downloads bar at the bottom of your web browser.When prompted, ensure the Enable Hyper-V Windows Features or the Install required Windows components for WSL 2 option is selected on the Configuration page.
Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to authorize the installer and proceed with the install.
When the installation is successful, click Close to complete the installation process.
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group. Run Computer Management as an administrator and navigate to Local Users and Groups > Groups > docker-users. Right-click to add the user to the group.Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
Start Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop, search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.
When the whale icon in the status bar stays steady, Docker Desktop is up-and-running, and is accessible from any terminal window.
If the whale icon is hidden in the Notifications area, click the up arrow on thetaskbar to show it. To learn more, see Docker Settings.
When the initialization is complete, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.

Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop on Windows.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Automatic updates
Starting with Docker Desktop 3.0.0, updates to Docker Desktop will be available automatically as delta updates from the previous version.
When an update is available, Docker Desktop automatically downloads it to your machine and displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version. All you need to do now is to click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows machine:
- From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Apps > Apps & features.
- Select Docker Desktop from the Apps & features list and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Important
Uninstalling Docker Desktop destroys Docker containers, images, volumes, andother Docker related data local to the machine, and removes the files generatedby the application. Refer to the back up and restore datasection to learn how to preserve important data before uninstalling.
Where to go next
- Getting started introduces Docker Desktop for Windows.
- Get started with Docker is a tutorial that teaches you how todeploy a multi-service stack.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, andhow to get support.
- FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
- Back up and restore data provides instructions on backing up and restoring data related to Docker.
Legacy desktop solution. Docker Toolbox is for older Mac and Windows systems that do not meet the requirements of Docker for Mac and Docker for Windows. We recommend updating to the newer applications, if possible.
Estimated reading time: 9 minutesDocker Toolbox provides a way to use Docker on olderWindows systems that do notmeet minimal system requirements for the Docker forWindows app.
If you have not done so already, download the installer here:
What you get and how it works
Docker Toolbox includes the following Docker tools:
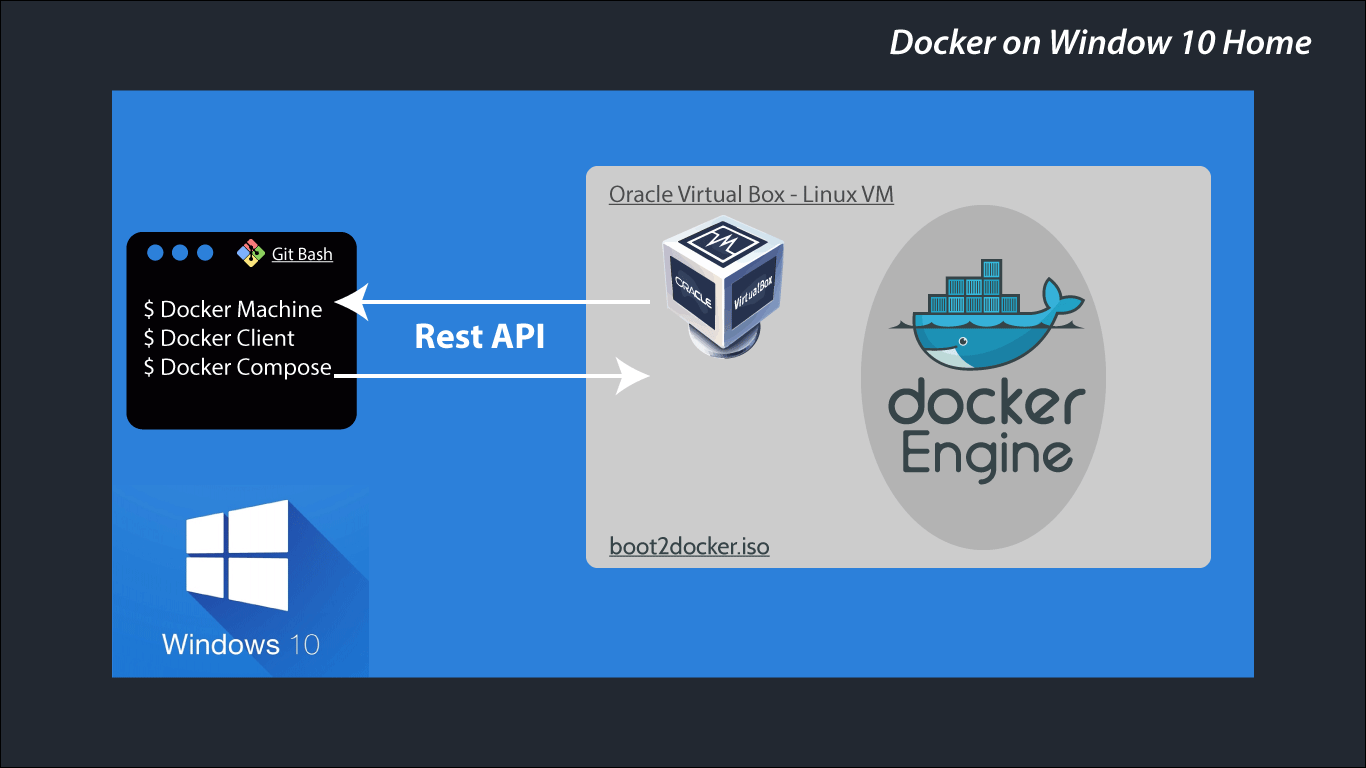
- Docker CLI client for running Docker Engine to create images and containers
- Docker Machine so you can run Docker Engine commands from Windows terminals
- Docker Compose for running the
docker-composecommand - Kitematic, the Docker GUI
- the Docker QuickStart shell preconfigured for a Docker command-line environment
- Oracle VM VirtualBox
Because the Docker Engine daemon uses Linux-specifickernel features, you can’t run Docker Engine nativelyon Windows. Instead, you must use the Docker Machinecommand, docker-machine, to create and attach to asmall Linux VM on your machine. This VM hosts Docker Enginefor you on your Windows system.
Tip: One of the advantages of the newerDocker forWindows solution is thatit uses native virtualization and does not requireVirtualBox to run Docker.
Download Docker Toolbox For Windows 10 Professional
Step 1: Check your version
To run Docker, your machine must have a 64-bit operating system running Windows 7 or higher. Additionally, you must make sure that virtualization is enabled on your machine.To verify your machine meets these requirements, do the following:

Right click the windows message and choose System.
If you aren’t using a supported version, you could consider upgrading your operating system.
If you have a newer system, specifically 64bit Windows 10 Pro, with Enterprise and Education (1511 November update, Build 10586 or later), consider using Docker for Windows instead. It runs natively on the Windows, so there is no need for a pre-configured Docker QuickStart shell. It also uses Hyper-V for virtualization, so the instructions below for checking virtualization will be out of date for newer Windows systems. Full install prerequisites are provided in the Docker for Windows topic in What to know before you install.
Make sure your Windows system supports Hardware Virtualization Technology and that virtualization is enabled.
For Windows 8 or 8.1Choose Start > Task Manager and navigate to the Performance tab. Under CPU you should see the following:
If virtualization is not enabled on your system, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for enabling it.
For Windows 7Run a tool like the Microsoft® Hardware-Assisted Virtualization Detection Tool or Speccy, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Verify your Windows OS is 64-bit (x64)
How you do this verification depends on your Windows version.
For details, see the Windows article How to determine whethera computer is running a 32-bit version or 64-bit version of theWindows operating system.
Step 2: Install Docker Toolbox
In this section, you install the Docker Toolbox software and several “helper” applications. The installation adds the following software to your machine:
- Docker Client for Windows
- Docker Toolbox management tool and ISO
- Oracle VM VirtualBox
- Git MSYS-git UNIX tools
If you have a previous version of VirtualBox installed, do not reinstall it with the Docker Toolbox installer. When prompted, uncheck it.
If you have Virtual Box running, you must shut it down before running theinstaller.
Go to the Docker Toolbox page.
Click the installer link to download.
Install Docker Toolbox by double-clicking the installer.
The installer launches the “Setup - Docker Toolbox” dialog.
If Windows security dialog prompts you to allow the program to make a change, choose Yes. The system displays the Setup - Docker Toolbox for Windows wizard.
Press Next to accept all the defaults and then Install.
Accept all the installer defaults. The installer takes a few minutes to install all the components:
When notified by Windows Security the installer will make changes, make sure you allow the installer to make the necessary changes.
When it completes, the installer reports it was successful:
Uncheck “View Shortcuts in File Explorer” and press Finish.
Step 3: Verify your installation
The installer adds Docker Toolbox, VirtualBox, and Kitematic to yourApplications folder. In this step, you start Docker Toolbox and run a simpleDocker command.
On your Desktop, find the Docker QuickStart Terminal icon.
Click the Docker QuickStart icon to launch a pre-configured Docker Toolbox terminal. Latest bootcamp drivers.
If the system displays a User Account Control prompt to allow VirtualBox to make changes to your computer. Choose Yes.
The terminal does several things to set up Docker Toolbox for you. When it is done, the terminal displays the
$prompt.The terminal runs a special
bashenvironment instead of the standard Windows command prompt. Thebashenvironment is required by Docker.Make the terminal active by clicking your mouse next to the
$prompt.If you aren’t familiar with a terminal window, here are some quick tips.
The prompt is traditionally a
$dollar sign. You type commands into thecommand line which is the area after the prompt. Your cursor is indicatedby a highlighted area or a|that appears in the command line. Aftertyping a command, always press RETURN.Type the
docker run hello-worldcommand and press RETURN.The command does some work for you, if everything runs well, the command’s output looks like this:
Looking for troubleshooting help?
Typically, the above steps work out-of-the-box, but some scenarios can cause problems. If your docker run hello-world didn’t work and resulted in errors, check out Troubleshooting for quick fixes to common problems.
Download Docker Toolbox For Windows 10 Protection
A Windows specific problem you might encounter has to do with the NDIS6 host network filter driver, which is known to cause issues on some Windowsversions. For Windows Vista systems and newer, VirtualBox installs NDIS6 driver by default. Issues can range from system slowdowns to networking problems for the virtual machine (VM). If you notice problems, re-run the Docker Toolbox installer, and select the option to install VirtualBox with the NDIS5 driver.
Download Docker Toolbox For Windows 10 Pro 64-bit
Optional: Add shared directories
By default, Toolbox only has access to the C:Users directory and mounts it intothe VMs at /c/Users.
Note: Within the VM path, c is lowercase and the Users is capitalized.
If your project lives elsewhere or needs access to otherdirectories on the host filesystem, you can add them, using the VirtualBox UI.
Open the VirtualBox UI.
Click the Settings gear, then go to Shared Folders.
Select any existing listing under Machine Folders, thenclick the + icon.
Choose the Folder Path on the host, enter the Folder Namefor within the VM (or take the default, which is the same nameas on the host), and configure any additional options you need.
Application loader xcode 11 download 32-bit. Choose Auto-mount if you want the folder to automaticallybe mounted into the VM, and choose Make Permanent for itto be considered a permanently shared folder.
Click OK to add the new folder to the Shared Folders list.
Click OK again to save your changes and exit the Settings dialog.
How to uninstall Toolbox
Removing Toolbox involves removing all the Docker components it includes.
A full uninstall also includes removing the local and remote machines you created with Docker Machine. In some cases, you might want to keep machines created with Docker Machine.
For example, if you plan to re-install Docker Machine as a part of Docker for Windows you can continue to manage those machines through Docker. Or, if you have remote machines on a cloud provider and you plan to manage them using the provider, you wouldn’t want to remove them. So the step to remove machines is described here as optional.
To uninstall Toolbox on Windows, do the following:
List your machines.
Optionally, remove each machine. For example:
This step is optional because if you planto re-install Docker Machine as a partof Docker forWindows, you can import andcontinue to manage those machinesthrough Docker.
Uninstall Docker Toolbox using Window’s standard process for uninstalling programs through the control panel (programs and features).
Note: This process does not remove the
docker-install.exefile. You must delete that file yourself.Optionally, remove the
C:Users<your-user>.dockerdirectory.If you want to remove Docker entirely, you can verify that the uninstall removed the
.dockerdirectory under your user path. If it is still there, remove it manually. This directory stores some Docker program configuration and/or state (e.g., information about created machines such as certificates). Removing this directory is typically not necessary.Uninstall Oracle VirtualBox, which is installed as a part of the Toolbox install.
Next steps
Macos catalina for unsupported macs. Try out the Get started tutorial.
Dig in deeper with more tutorials and examples on building images, running containers, networking, managing data, and storing images on Docker Hub.
Download Docker Toolbox For Windows 10 Home
docker, documentation, install, toolbox, win